Kubernetes Course Labs
Running a SQL Client in Kubernetes
Running databases inside Kubernetes isn't always the right choice, but it's great for non-production environments.
In that scenario you may not want your database accessible outside of the cluster, so if you need to run queries you can deploy Adminer - a web app which runs in a Pod, so it can connect to the Postgres database using the internal Service.
Deploy the Adminer SQL client
Deploy Adminer:
kubectl apply -f labs/statefulsets/specs/adminer
kubectl wait --for=condition=Ready pod -l app=adminer-web
Browse to http://localhost:8020 OR http://localhost:30020 and sign in:
- System (dropdown): PostgreSQL
- Server (already filled in): products-db-0.products-db.default.svc.cluster.local
- Username: postgres
- Password: w1dgetar!0
- Database: postgres
- Permanent login: checked
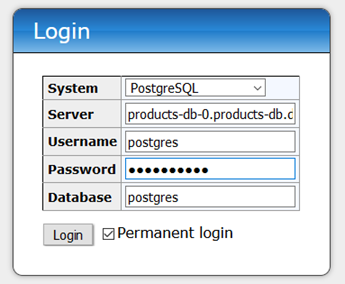
Now you;re connected to the database on the Primary Pod. You can browse to the Products table and see the data:
- http://localhost:8020/?pgsql=products-db-0.products-db.default.svc.cluster.local&username=postgres&db=postgres&ns=public&select=products (LoadBalancer)
OR:
- http://localhost:30020/?pgsql=products-db-0.products-db.default.svc.cluster.local&username=postgres&db=postgres&ns=public&select=products (NodePort)
Click the pencil icon in the Modify column and make a change to one row, like editing the name of a product:
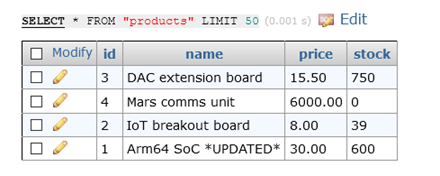
Now click Logout in the top right and log in again to the replica database server. The connection details are all the same except the server name, which uses the Service for Pod 1:
- Server: products-db-1.products-db.default.svc.cluster.local
Click select for the Products table and you'll see the change you made to the primary server has been replicated to the secondary. If you try to edit a row here you'll get an error message because the secondary is read-only.
Updating StatefulSets
Updating StatefulSets uses a consecutive rollout, starting from the last Pod in the set and moving backwards to the first. That means secondaries are replaced before the primary.
Some fields in the Pod spec are fixed (like the volume claim template), so you can't change those in an existing StatefulSet - you would need to remove and recreate it.
Other changes (container image, metadata etc.) are performed with consecutive Pod replacements:
- statefulset-with-pvc-annotation.yaml - adds an annotation to the Pod spec
Apply the update and watch the rollout happen in reverse:
kubectl apply -f labs/statefulsets/specs/products-db/update
kubectl get po -l app=products-db --watch
You'll see products-db-1 terminate and be replaced first, then products-db-0 when the new products-db-1 is running.
# Ctrl-C to extit the watch
kubectl get pvc -l app=products-db
The PVCs aren't changed - the new Pods attach to the original PVCs and the data is retained.
The consecutive rollout is more time-consuming but safer - if there's a problem with the rollout, the secondary may be unavailable but the primary will still be available.
Go back to the Adminer website and refresh your SQL query - the changes you made are still there, because the new Pods load the database files created by the previous Pods.
Cleanup
kubectl delete svc,cm,secret,statefulset,deployment,pod -l kubernetes.courselabs.co=statefulsets
Back to the exercises.